Pot Odds Table
Getting down the basic fundamentals of pot odds and implied odds will help you make better decisions in terms of the price you’re getting to continue. And being cognizant of reverse implied odds situations so you can look to avoid them and the costly spots they can put you in will help save you a lot of chips in the long run.
Display pertinent information on your table about players (stack,position,etc.), the table(pot odds,amount to call, etc.), and more. Customize the border colors to your liking to convey information about the status of the table. How Odds Work and 'The Long Shot' Let's say you're betting on a horse race and are given odds of 'seven to one', it will be written '7:1'. Odds conversion table with probability. Must be a number greater than 1. Must be a fraction, for example 2/1. Must be '+' or '-' and a whole number over 100. Must be a number from 0-100. By convention only a set of fractions are used in fractional odds betting markets. Pot odds, equity and expected value are important interrelated concepts in poker. As a beginner it is important that you understand the basics if you want to get ahead of your opponents. The math side of poker is often ignored by a lot of new players but by simply spending a bit of time learning these simple concepts you will be able to improve. Pot Odds The Rule of 4 and 2: Pot Odds Examples. Learning how to use pot odds puts an incredibly useful weapon in your poker arsenal. Knowledge of this basic concept is fundamental in determining whether or not you will become a winning or losing poker player.
Pot Odds
Pot Odds are simply the price that the pot is giving us to call right now, based on how much it is to stay in the pot and how much the pot will be after calling.
Example:
- The pot is 50. Your opponent bets another 50, so there is now 100 in the pot.
- It is 50 to call, so we are getting pot odds of 100-50, or simply 2-1 to call.
- In terms of equity, we are adding 33% to the pot. If we call and win the pot 33% of the time, we break even in the long run and this is an equitable call.
Here is a table of common pot odds calculations:
Implied Odds
Implied Odds refer to money that we can reasonably expect to win on future streets when improved to the best hand. These do take some additional estimation so may not be exact, but useful nonetheless.
We’ll use the example from above:
- You make the 50 call with suited connectors and you’ve flopped a flush draw.
- The chance to make the flush on the turn is roughly 4-1 (4.55-1, to be precise).
- You’re only getting 2-1 pot odds to call, so you’re not being given a good price to call with a flush draw.
- However, considering that there are still two more rounds of betting to come, you can reasonably expect to win more from making the call and turning the flush
Reverse Implied Odds

This one is more referential of a situation where the implied odds of continuing in the hand does not represent the true value, and you start to consider how much you will lose by making the desired hand because of the nature of the action that has taken place already.
For example:
- You bet 50 preflop with King-Jack offsuit.
- The Button 3-bets (reraises) you to 200. The price of calling is 150.
- Consider that your opponent’s typical 3-betting range will be cards which dominate your KJ. For instance, if the opponent holds AK/AA and the flop is king-high, or the opponent holds QQ/AJ and the flop is jack-high, you may well continue putting money into the pot with top-pair despite holding the losing hand.
- When KJ is winning, you don’t expect to see much value from future streets. For instance, against a small pocket pair, a jack-high board will limit the value which can be implied.
- Therefore, KJ is a hand which suffers from distinct Reverse Implied Odds. For similar reasons, this can also arise if you are calling to see a spade flush with one low spade, or you are on the low end of a straight-draw.
Conclusion

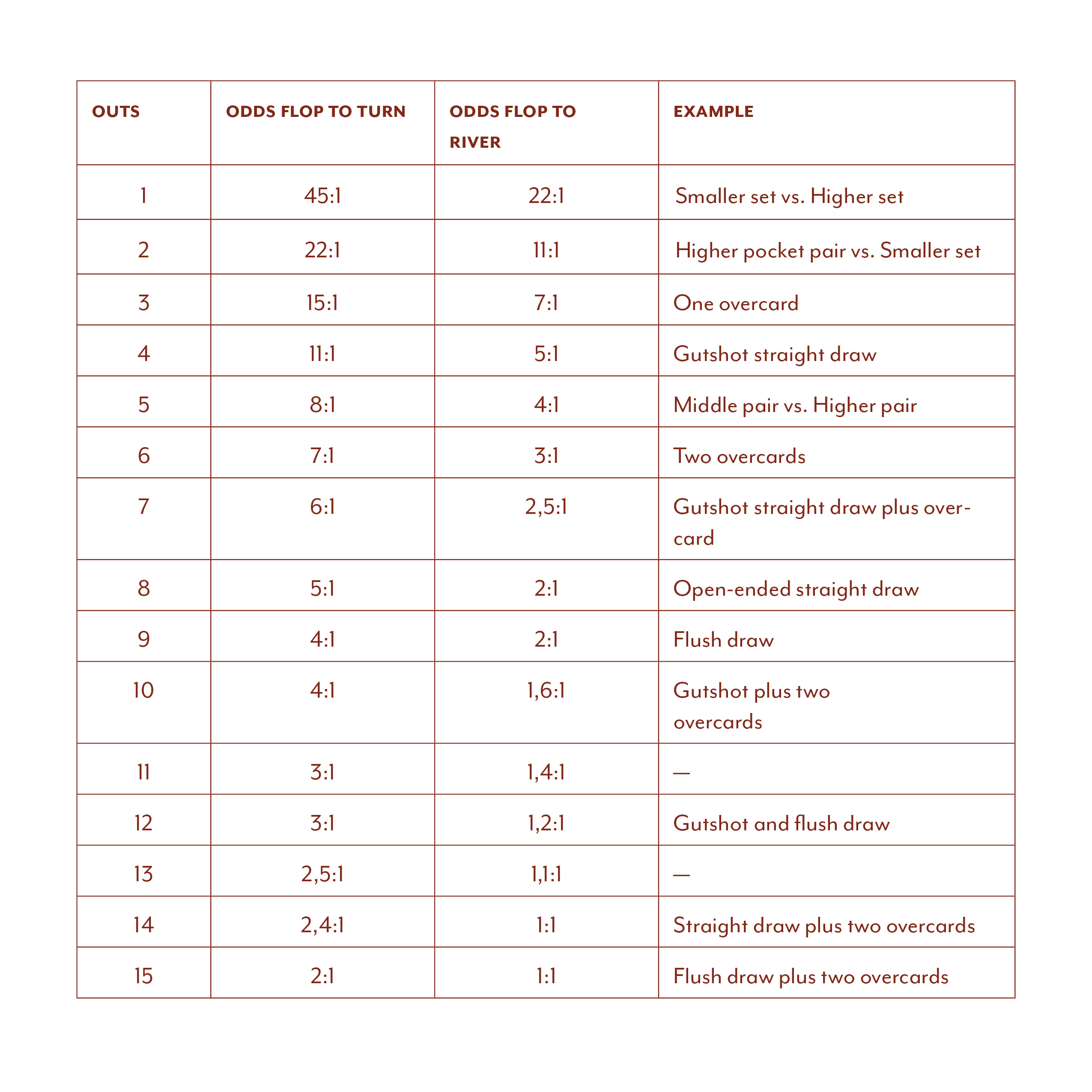
Calculating odds, outs and probabilities can seem difficult and time-consuming but the basics are quite simple and the ability to make simple calculations can help you build a very solid foundation for your game. This part of poker is worth learning, especially if you intend to progress further in the game.
.jpg)
If you continually play draws without getting the right odds, you will lose money in the long run. There will always be players who don’t care about odds and call too often. These players will occasionally get lucky and win a pot, but mostly they will lose and pay for it. On the other hand, you might be folding draws in situations where the odds are favorable.
Pot Odds Table
Test your knowledge with our short quiz below